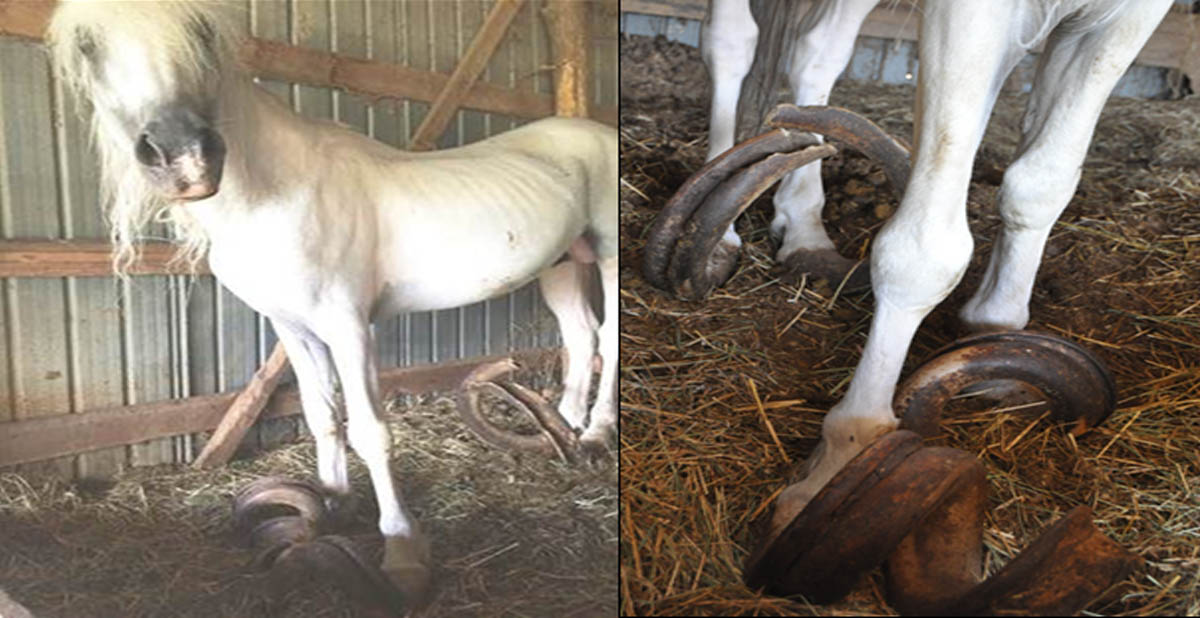
Stable Vices
Horses may develop damaging behaviors if they are suffering from boredom due to lack of exercise, isolation, excessive energy or hunger, or a nutritional imbalance. These actions are called `stable vices.` Kicking, weaving, wood chewing, and cribbing are the four most common vices.
Four Most Common Stable Vices
Kicking: Horses kept in stalls may begin kicking due to hunger or boredom. Kicking can destroy doors, walls, and feeders. This vice is easily taught to other horses. Horse owners can place toys, such as Jolly Stall Snack and Ball in the stall to discourage boredom, give the horse more turnout, or add a meal to their daily schedule.
Weaving: Weaving usually stems from boredom, but it is also another vice that can be a learned behavior. A horse that weaves will shift its weight from side to side and sway its head and neck. Weaving can cause weight loss, weakened tendons, and poor overall performance. Horses that are given extra turn out time will usually stop weaving.
Wood Chewing: Wood chewing is often due to boredom or a lack of exercise. However, wood chewing can cause abnormal wear on the teeth which in turn may lead to nutritional deficiencies and weight loss because the horse cannot chew properly. Wood chewing can be discouraged by providing a salt block as well as covering all wooden surfaces with deterrents such as Chew Stop
Cribbing: Cribbing is typically caused by boredom. A horse will set his incisors into an object such as a board or a bucket, arch his neck and pull backward as he swallows air. This action causes a release of endorphins. Cribbing can be very addictive and can also be a learned behavior. It can cause weight loss, colic, excessive tooth wear, and damage to stalls. Horse owners can use Chew Stop on surfaces to deter a horse from cribbing. Specifically designed collars, like Miracle Collar can also be used, but not all horses will tolerate a cribbing collar.
 Preventing Stable Vices
Preventing Stable Vices
If the horse owner`s accommodations allow, the horse owner should make an effort to reduce the amount of time the horse spends in a stall through turnout and regular exercise.
Horses are social animals. They do not cope with isolation well and may develop stable vices due to being alone. If possible, find a companion horse or another companion animal such as a goat, donkey, or a sheep, to keep the horse company. Horses that have companions are encouraged to display typical stimulating behaviors such as grooming each other and playing when turned out together.
 Horses require a diet that is largely roughage, but their diet must still meet their nutritional needs. All horses should be evaluated by a veterinarian before determining a suitable diet for the horse. Horses are fed based on their age, current bodyweight and future goal body weight, and performance level. If a horse does not receive adequate amounts of roughage, such as hay or grass, they can develop wood chewing or cribbing. When pasture grazing is not an option at the horse owner`s facility, it is best to provide several small meals each day. This may be accomplished by providing a hay net which encourages the horse to nibble and will reduce boredom. practices, emergency evacuation or `shelter in place` procedures for a facility, and how to be prepared for various natural disasters.
Horses require a diet that is largely roughage, but their diet must still meet their nutritional needs. All horses should be evaluated by a veterinarian before determining a suitable diet for the horse. Horses are fed based on their age, current bodyweight and future goal body weight, and performance level. If a horse does not receive adequate amounts of roughage, such as hay or grass, they can develop wood chewing or cribbing. When pasture grazing is not an option at the horse owner`s facility, it is best to provide several small meals each day. This may be accomplished by providing a hay net which encourages the horse to nibble and will reduce boredom. practices, emergency evacuation or `shelter in place` procedures for a facility, and how to be prepared for various natural disasters.
Horse Videos
Four Most Common Stable Vices
Kicking: Horses kept in stalls may begin kicking due to hunger or boredom. Kicking can destroy doors, walls, and feeders. This vice is easily taught to other horses. Horse owners can place toys, such as Jolly Stall Snack and Ball in the stall to discourage boredom, give the horse more turnout, or add a meal to their daily schedule.
Weaving: Weaving usually stems from boredom, but it is also another vice that can be a learned behavior. A horse that weaves will shift its weight from side to side and sway its head and neck. Weaving can cause weight loss, weakened tendons, and poor overall performance. Horses that are given extra turn out time will usually stop weaving.
Wood Chewing: Wood chewing is often due to boredom or a lack of exercise. However, wood chewing can cause abnormal wear on the teeth which in turn may lead to nutritional deficiencies and weight loss because the horse cannot chew properly. Wood chewing can be discouraged by providing a salt block as well as covering all wooden surfaces with deterrents such as Chew Stop
Cribbing: Cribbing is typically caused by boredom. A horse will set his incisors into an object such as a board or a bucket, arch his neck and pull backward as he swallows air. This action causes a release of endorphins. Cribbing can be very addictive and can also be a learned behavior. It can cause weight loss, colic, excessive tooth wear, and damage to stalls. Horse owners can use Chew Stop on surfaces to deter a horse from cribbing. Specifically designed collars, like Miracle Collar can also be used, but not all horses will tolerate a cribbing collar.

If the horse owner`s accommodations allow, the horse owner should make an effort to reduce the amount of time the horse spends in a stall through turnout and regular exercise.
Horses are social animals. They do not cope with isolation well and may develop stable vices due to being alone. If possible, find a companion horse or another companion animal such as a goat, donkey, or a sheep, to keep the horse company. Horses that have companions are encouraged to display typical stimulating behaviors such as grooming each other and playing when turned out together.

Share with your friends
Horse Videos